There are many advantages to storing data in the cloud. It offers flexibility, scalability, and reduces the maintenance burden on in-house IT staff. However, more and more organizations are choosing to move back from the cloud to their own data centers: “Cloud repatriation” is the process of bringing data, applications, and workloads that have been outsourced to a public cloud back into your own infrastructure.
In this article, we will discuss the reasons why you may want to move away from the public cloud. We explain what you need to consider for a successful migration and implementation of a private or hybrid cloud.
Data Security and Compliance
Data sovereignty is a key issue in connection with cloud repatriation – in other words, control over your own data and the security measures to protect this data.
- Security breaches at cloud providers show that data security is not always as high as companies expected when they moved to the cloud.
- When customers’ personal information is compromised in a security incident, it can be extremely damaging to a company’s image. Compliance with data protection regulations is often a reason for companies to bring data from the cloud back into their own infrastructure.
- Sensitive corporate data also deserves special protection, which the company should be able to determine for itself.
Cost and Performance Optimization
Organizations using cloud storage are often faced with data growth that was not anticipated when planning their cloud strategy.
- Unexpectedly high costs for transaction fees, storage fees, and egress fees can cause organizations to rethink their cloud storage strategy.
The situation is similar for performance and availability requirements.
- To reliably access large amounts of data in the cloud, you need a fast and stable Internet connection. These requirements are often not met when reading data from the cloud.
Bring Cloud Data Home: Goals
The motivations and goals of cloud repatriation are therefore wide-ranging:
- Reducing dependence on external service providers
- More control over your data and its security
- Compliance with privacy regulations
- Costs reduction
- Fulfillment of performance and latency requirements
Strategies for Successful Cloud Repatriation
A properly prepared infrastructure in the local data center is critical for a seamless and successful cloud repatriation. The infrastructure of the private cloud must be as close as possible to the structures of the public cloud in order to benefit from the advantages of cloud storage in-house.
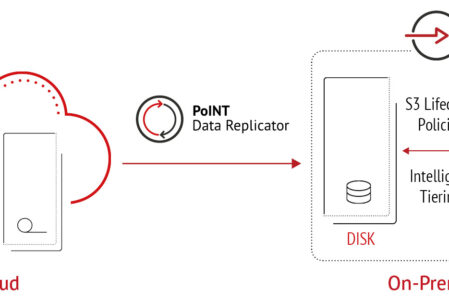
The starting point is S3 object storage with storage class differentiation, analogous to the different storage classes offered by cloud providers:
- On-premises data is also stored via the standardized S3 interface. This enables the seamless data migration and adaptation of applications.
- An S3-to-Tape solution, i.e. the integration of tape via the S3 interface, meets the cost efficiency requirements. Tape is ideal for long-term storage of large volumes of inactive data.
- A solution that integrates a disk and tape storage class under a single namespace is particularly efficient. This provides the optimal storage class for productive and inactive data, respectively. The structure of the public cloud is thus implemented on-premises as a private cloud.
Advantages of the Private Cloud with Storage Class Differentiation
The S3 integration of an object storage solution that offers multiple storage classes under a single namespace allows you to bring the benefits of cloud storage into your local data center.
- Maximum flexibility:
A standardized interface gives you the flexibility to design and optimize your individual cloud solution, whether it is a pure private cloud or a hybrid cloud. - Cost and energy efficiency:
Data storage on tape offers high levels of cost and energy efficiency. In our blog post “Storage infrastructure sustainability through tape integration with intelligent software” (Link), we explain the specific benefits of a tape storage class, especially for storing large volumes of inactive data. - Cybersecurity and compliance:
By integrating a tape storage class into your private cloud, you increase the cybersecurity of your data assets. Due to its offline capability and physical air gap, tape is considered the “last line of defense” against ransomware threats.